How LoRaWan Outshines 5G for Cost-Effective, Energy-Efficient IoT Solutions
LoRaWan, an ideal technology for prototyping applications for the Internet of Things
When we talk about the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G regularly comes to the fore. At first glance, a fast network capable of carrying large amounts of data is perfect for such
applications.
However, this view overlooks the fact that this solution is expensive, oversized for most needs and, most importantly, energy hungry. What's more, it requires a SIM card to be physically installed in devices: a major obstacle to widespread deployment.
That's where LoRaWan comes in. LoRaWan, which stands for long-range wide-area network, is an open-source technology owned by the non-profit LoRa Alliance. Its aim is to standardise the network on the basis of contributions from hundreds of enthusiasts who are hard at work
improving it!
What is LoRa?
LoRa is a wireless (radio) communication protocol developed for long-distance, low-energy consumption applications. From a technical point of view, this method makes it possible to encode information on radio waves using pulses.
LoRaWan is the name given to a network that uses this radio language. In this network, each terminal sends its information to an application server, which in turn transmits it to a central server. Precision is important: by grouping the signals and comparing their arrival times, these intermediate servers can geolocate where the information is coming from, so they can easily find out which terminal to send a response to. LoRaWan networks are ideal for applications that transmit small amounts of information at low data rates LoRaWan networks are. However, depending on the radio frequencies used, they can transmit data at higher speeds at the expense of range. In simple terms, this technology could be described as being able to transmit information over a distance as long as a cellular network such as 5G, but at limited speeds.
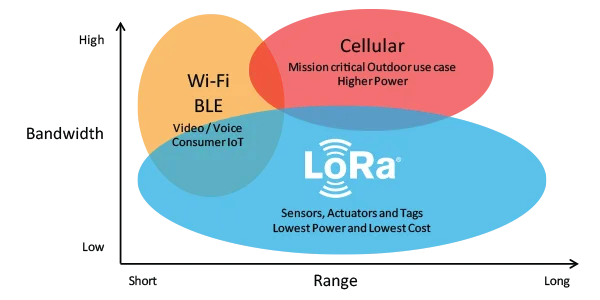
The benefits of LoRaWan
Networks using the LoRa protocol have a number of advantages:
- Lower operating costs by using free radio frequency bands and therefore no subscription fees;
- The possibility of setting up private networks, i.e. independent of operators;
- Energy savings: sensors can last up to ten years without battery replacement. This is because they only communicate when requested by the server, or only sporadically;
- Longer range than WiFi or Bluetooth. This can be up to 10 kilometers in rural areas. In urban areas, interference limits its effectiveness to 3 kilometers. The reason for this is that LoRaWan is sensitive to interference (hills in the line of sight, reflections from buildings, etc.);
- There are few problems with indoor use on multiple floors. LoRaWan receivers (or gateways) can be added to your own premises at low cost;
- Multiple messaging: connected terminals can send millions of messages;
- Possibility of geolocation of objects thanks to triangulation: when several LoRaWan gateways receive the same message, they transmit it to the central application server, which is able to determine the position of the sender on the map thanks to latency times;
- Secure data transmission: several keys (NwkSKey and AppSKey) are used to ensure the security of the exchanges. In particular, these make it possible to check that the data transmitted has not been tampered with by malicious devices;
- Open source: LoRA is continuously extended by the community under the umbrella of major industrial groups.
In what context can LoRa be used?
The qualities of LoRA make this communication protocol particularly useful in many contexts. Here are some of the areas in which it can be used (the list is not exhaustive):
- Respect of the cold chain: The transport of certain foodstuffs or medicines is subject to the maintenance of a minimum temperature. The LoRaWan system ensures that this temperature is maintained throughout the entire transport process. A clear gain in transparency and service quality;
- Agriculture: Terminals can transmit soil moisture in real time. This information can be used to optimise crop irrigation and significantly reduce water consumption;
- Water networks: terminals can identify leaks. By multiplying the number of terminals, the location of the leak can be pinpointed, allowing the necessary repairs to be carried out as quickly as possible;
- Fleet management: equipping vehicles with tracking devices can optimise routes, reduce fuel consumption and ensure on-time deliveries. (See the Case Study about Hyperio's fleet management solution).
- Remote meter reading for energy supply companies: LoRaWan makes manual meter reading a thing of the past;
- Noise and air quality monitoring in urban areas: information on environmental conditions could help inform policy decisions to improve public health;
- Energy management: by monitoring energy consumption in real time, potential improvements can be identified.

Which service provider should I use to set up a LoRaWan system?
In Switzerland, various service providers offer products using the LoRa protocol. Here are Hyperio's favourites:
Swisscom LPN (Low Power Network)
- Coverage: Swisscom has solid national coverage thanks to an extensive network of LoRaWan gateways. It reaches 97% of the country's populated areas.
- Price: Swisscom offers connectivity services on a pay-as-you-go basis, with offers tailored to the volume of data and number of connected devices.
- Accessibility: Pay-as-you-go subscriptions make this solution very accessible to businesses and individuals. The good news is that Hyperio owns the licence to add nodes (IoT devices and data management services) to the network.
The Things Network (TTN)
- Coverage: TTN is a global community network with a strong presence in Switzerland. Its coverage depends on local contributions.
- Price: This service is free as it is based on a community approach. Users install and share their own gateways.
- Accessibility: TTN is accessible to everyone, but is particularly suitable for small companies, developers and individual projects. Depending on the density of gateways installed by the local community, Hyperio can install local gateways to amplify the signal.
Helium
This decentralised wireless network deserves a closer look. Helium's ambition is to create a global network accessible to all, allowing IoT devices to connect to the internet through a network of user-owned gateways.
The project stands out for its unique economic and technological model, which combines blockchain and financial incentives to increase the number of participants in the network.
How does it work?
- Users buy Helium gateways, called hotspots. Once installed, they act as relays between IoT devices and the internet, using LoRa for long-range communications;
- Helium uses a native cryptocurrency called HNT, for Helium Network Token. Hotspot owners earn HNTs by providing network coverage and relaying data from IoT devices. These rewards are proportional to the amount of data relayed and the quality of coverage provided;
- Helium uses a 'proof of coverage' mechanism to verify that hotspots are actually providing network coverage. Hotspots validate their presence and performance by randomly sending and receiving signals that are verified by the network.
It's easy to see the benefits of such a system. Helium could provide global LoRaWan coverage, enabling IoT devices to operate in areas poorly served by traditional networks, while reducing connectivity costs. In any case, they will remain lower than those of cellular networks. Finally, thanks to its community approach and business model, Helium encourages users to contribute to the network and earn rewards.

LoRA's limitations
There's no such thing as a perfect communication system. LoRaWan networks are no exception. Here are some of the drawbacks of this technology:
- Interference: As long-distance networks proliferate, spectrum interference can occur between them.
- The need to build a new network: The strength of LoRa is that it does not depend on an operator, which is also a weakness. While it is cheap to operate, it requires some investment to deploy in areas where free networks (such as TTN) are not available. However, this investment remains modest if you want to test the effectiveness of your project first (Akenza, for example, offers demonstration packages). It can easily be expanded later with private gateways.
Ultimately, the deployment of LoRaWan is a response to a critical issue in the development of the IoT: energy consumption. The architecture of these networks should unlock the potential for information sharing between connected objects. Because they are cost-effective, secure and efficient, LoRa-based networks are set to be deployed on a large scale. Given their relatively low cost, it is in the interest of the business community to test them.
Related articles
Nemo, a tailor-made AI for companies and public authorities
IoT and logistics: save money and improve working conditions
Liked this article?
Share it with the world!
Contact us
Lets' get in touch
Are you looking for a partner to realize your ambitions? Hyperio specializes in delivering tailored software solutions, IT consulting, and digital transformation services to help your business thrive.


